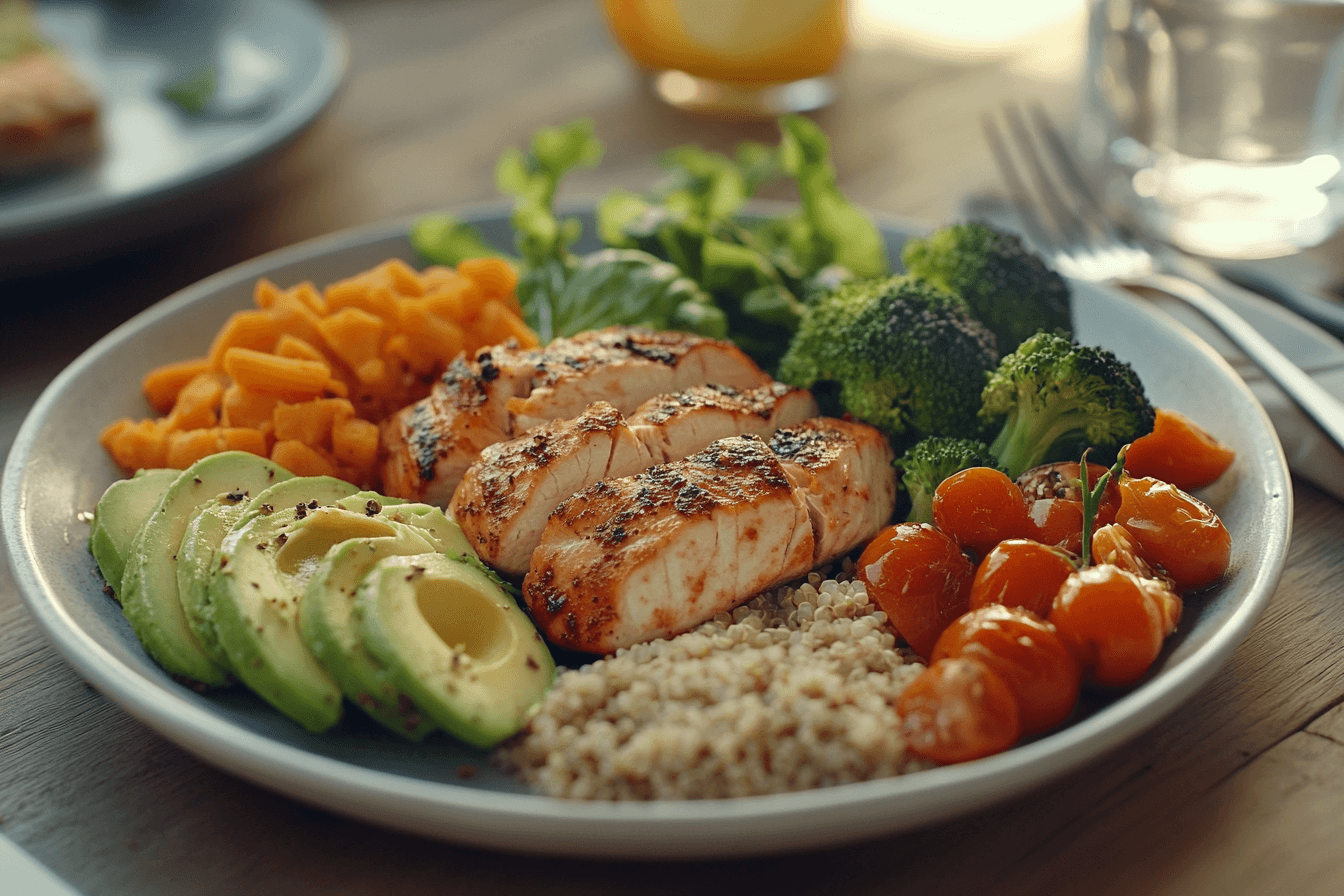Discover the balanced approach of the 40 40 20 meal plan, perfect for a healthy lifestyle.
The 40 40 20 meal plan is a structured dietary strategy that divides daily calorie intake into specific macronutrient ratios. This approach ensures a balanced distribution of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, promoting overall health and wellness. Moreover, adhering to these proportions allows individuals to achieve their nutritional goals while maintaining flexibility in their meal choices.
What Defines the 40 40 20 Meal Plan?
The 40 40 20 meal plan allocates 40% of daily calories to carbohydrates, 40% to proteins, and 20% to fats. This balance supports energy levels, muscle maintenance, and essential bodily functions. Unlike other diets that may emphasize one macronutrient over others, the 40 40 20 approach provides a comprehensive framework that caters to diverse dietary needs and preferences.
Carbohydrates: 40% of Daily Intake
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. On this meal plan, they account for 40% of daily calories, focusing on complex carbs like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes. Additionally, complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy, essential fiber, and a range of vitamins and minerals necessary for optimal bodily functions. Examples include:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats
- Vegetables: Broccoli, sweet potatoes, spinach
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans
Consequently, incorporating these sources ensures a steady release of energy, preventing blood sugar spikes and crashes that can lead to fatigue and cravings.
Proteins: 40% of Daily Intake
Proteins are crucial for muscle repair and growth. Allocating 40% ensures adequate intake from lean meats, dairy, and plant-based sources, supporting an active lifestyle. Furthermore, protein is essential for hormone production, enzyme function, and immune system support. Key protein sources include:
- Lean Meats: Chicken breast, turkey, lean beef
- Dairy: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, low-fat milk
- Plant-Based: Tofu, tempeh, edamame
By maintaining a high protein intake, the meal plan aids in muscle synthesis, enhances satiety, and helps in weight management by reducing overall calorie consumption through increased fullness.
Fats: 20% of Daily Intake
Fats are essential for hormone production and nutrient absorption. The 40 40 20 meal plan emphasizes healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Moreover, healthy fats play a vital role in maintaining cell structure, protecting organs, and providing a concentrated energy source. Recommended fat sources include:
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats and fiber
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds
- Healthy Oils: Olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil
Incorporating these fats ensures that the body receives the necessary fatty acids without excessive calorie intake, promoting heart health and cognitive function.
Benefits of the 40 40 20 Meal Plan
Adopting the 40 40 20 meal plan offers numerous advantages for health and well-being. Additionally, this balanced approach not only supports physical health but also enhances mental clarity and overall quality of life.
Balanced Nutrition for Optimal Health
This meal plan provides a well-rounded intake of essential nutrients, reducing the risk of deficiencies and supporting overall bodily functions. By evenly distributing macronutrients, individuals can ensure they receive adequate vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients necessary for maintaining health. Balanced nutrition helps in:
- Preventing Deficiencies: Ensures intake of essential vitamins and minerals
- Supporting Metabolic Functions: Facilitates efficient metabolism and energy production
- Enhancing Immune Function: Strengthens the body’s defense mechanisms against illnesses
Weight Management and Metabolic Health
Furthermore, by controlling macronutrient ratios, the 40 40 20 meal plan aids in maintaining a healthy weight and improving metabolic health, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases. Balanced macronutrient distribution helps in:
- Promoting Satiety: High protein and fiber intake reduce hunger and prevent overeating
- Boosting Metabolism: Adequate protein supports muscle mass, which in turn enhances metabolic rate
- Reducing Risk of Chronic Diseases: Balanced diet lowers the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension
Enhanced Energy Levels and Mental Clarity
A balanced distribution of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats ensures sustained energy throughout the day, enhancing productivity and mental focus. Consistently, energy levels prevent the afternoon slump and improve overall cognitive function. Benefits include:
- Improved Concentration: Steady energy supply supports brain function and focus
- Reduced Fatigue: Balanced nutrients prevent energy crashes and maintain vitality
- Enhanced Mood: Proper nutrition supports neurotransmitter function, influencing mood and mental health
Flexibility and Sustainability
The 40 40 20 meal plan is adaptable to various lifestyles and dietary preferences, making it a sustainable long-term approach. Whether you follow a vegetarian, vegan, or omnivorous diet, this meal plan can be tailored to suit your needs. Its flexibility allows for:
- Diverse Food Choices: Incorporate a wide range of foods to prevent dietary monotony
- Personalization: Adjust macronutrient ratios slightly based on individual goals and preferences
- Ease of Adherence: Simple guidelines make it easier to stick to the plan without feeling restricted
Implementing the 40 40 20 Meal Plan
Successfully following the 40 40 20 meal plan involves careful planning and mindful eating habits. Therefore, here are some steps and tips to help you integrate this meal plan into your daily routine effectively.
Calculating Your Daily Caloric Needs
Determine your daily caloric requirements based on factors like age, gender, weight, and activity level to effectively allocate macronutrients. This ensures that you consume the right amount of calories to meet your health goals, whether it’s weight loss, maintenance, or muscle gain. Tools like the Harris-Benedict equation or online calorie calculators can assist in this process.
Example Calculation for a 2000-Calorie Diet
- Carbohydrates: 40% of 2000 = 800 calories (200 grams)
- Proteins: 40% of 2000 = 800 calories (200 grams)
- Fats: 20% of 2000 = 400 calories (44 grams)
This example provides a clear framework for daily intake, making it easier to plan meals and track macronutrients accurately.
Meal Planning and Preparation Tips
Plan meals in advance to ensure balanced macronutrient distribution. Additionally, incorporate a variety of foods to meet nutritional needs and prevent dietary monotony. Effective meal planning involves:
- Creating a Weekly Menu: Outline meals for the week to ensure variety and balance
- Grocery Shopping: Buy ingredients that fit the macronutrient ratios, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods
- Batch Cooking: Prepare meals in bulk to save time and maintain consistency
Incorporate Diverse Food Sources
Include a mix of vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats in your meals to achieve the desired macronutrient balance. Consequently, diversity in food sources ensures that you receive a broad spectrum of nutrients, promoting overall health.
Monitor Portion Sizes
Monitor Portion Sizes
Therefore, use measuring tools or portion control techniques to maintain accurate macronutrient ratios and avoid overeating. Additionally, portion control plays a crucial role in preventing calorie excess. Consequently, it ensures that each meal aligns with the 40 40 20 meal plan distribution. Moreover, by consistently monitoring your portions, you can better manage your daily intake. As a result, this practice supports your nutritional goals and promotes sustainable eating habits.
Adapting the Meal Plan to Your Lifestyle
Customize the 40 40 20 meal plan to fit your daily routine, dietary preferences, and specific health goals for maximum adherence and effectiveness. Consider factors such as:
- Work Schedule: Plan meals that are easy to prepare and consume during busy days
- Exercise Routine: Adjust protein intake on workout days to support muscle recovery
- Personal Preferences: Incorporate favorite foods within the macronutrient guidelines to enhance enjoyment
Sample 40 40 20 Meal Plan
To help you get started, here’s a sample meal plan that follows the 40 40 20 meal plan ratios. This plan includes breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks, ensuring balanced macronutrient distribution throughout the day.
Breakfast
- Oatmeal with Berries and Almonds
- Carbohydrates: 1 cup of cooked oatmeal
- Proteins: 2 tablespoons of almond butter
- Fats: 1 ounce of almonds
- Greek Yogurt
- Carbohydrates: Fresh berries
- Proteins: 1 cup of Greek yogurt
- Fats: Drizzle of honey
Mid-Morning Snack
- Protein Smoothie
- Carbohydrates: 1 banana
- Proteins: 1 scoop of protein powder
- Fats: 1 tablespoon of flaxseeds
Lunch
- Grilled Chicken Salad
- Carbohydrates: Mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers
- Proteins: 6 ounces of grilled chicken breast
- Fats: 2 tablespoons of olive oil-based dressing
- Quinoa
- Carbohydrates: 1 cup of cooked quinoa
Afternoon Snack
- Hummus and Veggie Sticks
- Carbohydrates: Carrot and celery sticks
- Proteins: 1/4 cup of hummus
- Fats: Olive oil in hummus
Dinner
- Baked Salmon with Sweet Potatoes and Asparagus
- Carbohydrates: 1 medium sweet potato
- Proteins: 6 ounces of baked salmon
- Fats: 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- Steamed Asparagus
- Carbohydrates: Asparagus spears
- Proteins: Minimal
- Fats: Drizzle of lemon juice and olive oil
Evening Snack
- Cottage Cheese with Pineapple
- Carbohydrates: Pineapple chunks
- Proteins: 1 cup of cottage cheese
- Fats: Minimal
This sample meal plan illustrates how to distribute macronutrients across meals and snacks, ensuring that each component aligns with the 40 40 20 ratios.
Tools and Resources for Success
Utilizing tools and resources can greatly enhance your ability to follow the 40 40 20 meal plan effectively. Moreover, these tools help in tracking intake, planning meals, and staying motivated.
Meal Planning Apps
Apps like MyFitnessPal, Cronometer, and Lose It! allow you to track your daily intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These platforms often provide features such as:
- Barcode Scanning: Quickly log packaged foods
- Recipe Importing: Add homemade recipes and calculate macronutrients
- Goal Setting: Set and monitor personal nutrition goals
Difficulty in Balancing Macronutrients
Solution: Utilize meal planning apps or consult a nutritionist to help distribute macronutrients accurately across meals. Additionally, preparing meals in advance and using measuring tools can ensure that each meal aligns with the 40 40 20 ratios.
Limited Food Choices or Dietary Restrictions
Solution: Adapt the meal plan by selecting alternative foods that fit within the macronutrient framework, ensuring nutritional needs are still met. For example, if you’re vegetarian, focus on plant-based protein sources like tofu, legumes, and tempeh.
Managing Social Situations and Eating Out
Solution: Plan ahead by researching restaurant menus and making informed choices that align with the 40 40 20 meal plan ratios. Opt for dishes that offer balanced macronutrients, such as grilled proteins with vegetables and whole grains.
Time Constraints for Meal Preparation
Solution: Incorporate batch cooking and meal prepping techniques to save time during the week. Prepare large quantities of staples like quinoa, grilled chicken, and roasted vegetables that can be easily assembled into balanced meals.
Maintaining Motivation and Consistency
Solution: Set realistic goals and track your progress to stay motivated. Engaging with a community or finding a meal plan buddy can provide support and accountability, making it easier to maintain consistency.
Comparing the 40 40 20 Meal Plan to Other Diets
Understanding how the 40 40 20 meal plan stands against other dietary approaches can help in making informed decisions. Here’s a comparison with some popular diets.
40 40 20 vs. Low-Carb Diets
While low-carb diets restrict carbohydrate intake, the 40 40 20 meal plan allows a higher carbohydrate percentage, providing more energy and variety. Low-carb diets often focus on reducing carbs to promote fat loss, which can lead to:
- Potential Energy Deficits: Limited carbohydrates may result in lower energy levels, especially for active individuals
- Restricted Food Choices: Fewer options for fruits, grains, and certain vegetables
In contrast, the 40 40 20 meal plan offers a more balanced approach, ensuring adequate carbohydrate intake for sustained energy and a wider range of food choices.
40 40 20 vs. High-Protein Diets
Unlike high-protein diets that may excessively focus on proteins, the 40 40 20 meal plan maintains a balanced approach, preventing potential health issues related to excessive protein consumption. High-protein diets can sometimes lead to:
- Kidney Strain: Excessive protein intake may burden the kidneys over time
- Nutrient Imbalances: Neglecting carbohydrates and fats can result in deficiencies and imbalances
The plan ensures that proteins are consumed in moderation alongside adequate carbohydrates and fats, promoting overall health without the risks associated with extreme macronutrient ratios.
40 40 20 vs. Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes healthy fats, whole grains, and lean proteins, similar to the 40 40 20 meal plan. However, the Mediterranean diet may have more flexibility in fat intake and specific food preferences. The key differences include:
- Focus on Specific Foods: The Mediterranean diet highlights foods like olive oil, fish, and fresh vegetables more prominently
- Cultural Emphasis: Rooted in the traditional eating patterns of Mediterranean countries
Both diets promote balanced nutrition and healthy eating habits, but the 40 40 20 meal plan offers a more defined macronutrient structure, which can be beneficial for those seeking specific nutritional ratios.
40 40 20 vs. Paleo Diet
The Paleo diet focuses on whole, unprocessed foods, excluding grains, legumes, and dairy. In contrast, the 40 40 20 meal plan includes a wider variety of food groups, allowing for more flexibility. Key differences include:
- Food Inclusion: The Paleo diet excludes certain food groups that are included in the 40 40 20 meal plan
- Macronutrient Flexibility: The plan provides specific macronutrient ratios, while the Paleo diet is more focused on food quality and exclusion
Therefore, the 40 40 20 meal plan offers a balanced macronutrient approach suitable for a broader audience, whereas the Paleo diet is more restrictive and tailored to specific dietary philosophies.
Tips for Success on the 40 40 20 Meal Plan
Implementing the 40 40 20 meal plan successfully requires dedication and strategic planning. Here are some actionable tips to help you stay on track and maximize the benefits of this meal plan.
Prioritize Whole, Unprocessed Foods
Focusing on whole foods ensures that you receive maximum nutrients without unnecessary additives or preservatives. Furthermore, whole foods are typically more nutrient-dense and can help you feel fuller longer, supporting your satiety goals. Examples include:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread
- Lean Proteins: Chicken breast, turkey, tofu
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, olive oil
Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is essential for overall health and can aid in weight management by reducing hunger and boosting metabolism. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and consider:
- Infused Water: Add lemon, cucumber, or mint for flavor without extra calories
- Herbal Teas: A flavorful alternative to plain water
- Avoid Sugary Beverages: Limit intake of sodas and sweetened drinks that can add unnecessary calories
Incorporate Regular Physical Activity
Combining the 40 40 20 meal plan with regular exercise can enhance weight loss, improve muscle tone, and boost overall health. Activities can include:
- Cardio Exercises: Running, cycling, swimming for cardiovascular health
- Strength Training: Weightlifting or bodyweight exercises to build muscle
- Flexibility and Balance: Yoga or Pilates to improve flexibility and reduce injury risk
Monitor Your Progress
Keeping track of your progress helps in maintaining motivation and making necessary adjustments. Consider:
- Journaling: Record your meals, workouts, and how you feel each day
- Regular Weigh-Ins: Monitor your weight at consistent intervals
- Body Measurements: Track changes in waist circumference, muscle mass, and other metrics
Seek Support and Accountability
Having a support system can significantly enhance your adherence to the meal plan. Ways to find support include:
- Joining Online Communities: Engage with others following the 40 40 20 meal plan
- Finding a Meal Plan Buddy: Partner with someone who shares your goals
- Consulting a Professional: Work with a dietitian or nutritionist for personalized guidance
Frequently Asked Questions
Is 1400 calories realistic?
Absolutely, a 1400-calorie diet can be realistic and effective for weight loss or maintenance, depending on individual needs and activity levels. It’s important to ensure that even with a lower calorie intake, the diet remains balanced and provides all necessary nutrients. Therefore, consulting with a healthcare provider before starting a 1400-calorie diet is recommended to ensure it aligns with your personal health goals and requirements.
How to stay full on 1400 calories a day?
To stay full on 1400 calories, focus on high-fiber foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Additionally, incorporate plenty of vegetables and whole grains to maintain satiety. Strategies include:
- Eating Fiber-Rich Foods: Vegetables, fruits, and whole grains can help you feel fuller longer
- Including Protein in Every Meal: Protein promotes satiety and reduces overall hunger
- Choosing Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, and olive oil can help keep you satisfied between meals
Moreover, drinking plenty of water and spacing meals evenly throughout the day can help manage hunger effectively.
What does a 1400-calorie diet consist of?
A 1400-calorie diet typically includes balanced portions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, emphasizing nutrient-dense foods like vegetables, lean meats, whole grains, and healthy fats. A sample distribution might align with the 40 40 20 ratios, ensuring that each meal contributes to the overall macronutrient goals while staying within the calorie limit. This approach helps in maintaining energy levels and preventing nutrient deficiencies despite the lower calorie intake.